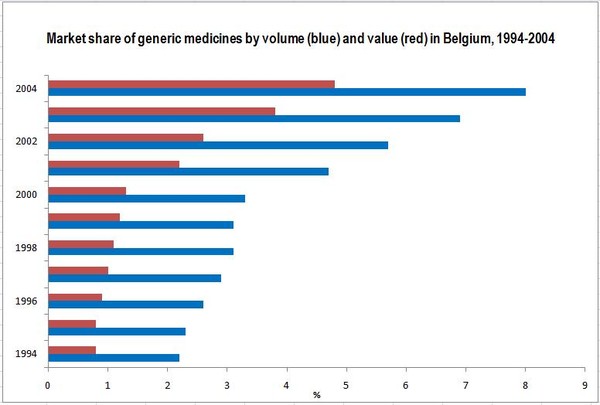
Belgium had a small generic medicines market during the second half of the 1990s. Its development was boosted by the introduction of a reference-pricing system in 2001. Public expenditure on generic medicines rose from Euros 18 million in 1994 (market share by value of 0.8%) to Euros 213 million in 2004 (market share of 4.8%) [1].
The market share of generic medicines by volume nearly quadrupled from 2.2% in 1994 to 8.0% in 2004 [1].
Source: 1994–2004 [1]
In Belgium, control is exercised over the prices of all medicines. This control can take
the form of either price fixing or price notification, depending on the type of medicine [2].
Physicians in Belgium are not trained at medical school to write prescriptions by international non-proprietary name (INN). However, since 2006 physicians have been required to prescribe minimum percentages of low-cost prescriptions (so-called ‘quotas’) in order to benefit from the savings due to the lower costs of generics [5].
In 2008, only 3% of prescriptions in Belgium were written by INN [6].
Highlights of the generics market in Belgium
- The market share of generic medicines by volume (prescriptions) in 2008 was only 8.8%, representing around 5% in market value [1].
- Physicians are obliged to prescribe a certain amount of low-priced medicines [3].
- Substitution by the pharmacist is allowed if the prescription is written by INN and if the patient agrees with substitution [4].
References
1. Simoens S, De Coster S. Sustaining Generic Medicines Markets in Europe. April 2006. [monograph on the Internet]. Brussels, Belgium, European Generic Medicines Association (EGA) [cited 2011 May 13]. Available from: www.egagenerics.com/doc/simoens-report_2006-04.pdf
2. Österreichisches Bundesinstitut für Gesundheitswesen (ÖBIG). Surveying, Assessing and Analysing the Pharmaceutical Sector in the 25 EU Member States. July 2006.
3. Österreichisches Bundesinstitut für Gesundheitswesen (ÖBIG). Rational use of medicines Europe. February 2010.
4. Federaal Kenniscentrum voor de Gezondheidszorg (Belgian Healthcare knowledge centre [KCE]). The reference price system and socioeconomic differences in the use of low cost drugs. KCE reports 126C. 2010.
5. Simoens S. Generic medicine pricing in Europe: current issues and future perspectives. JME. 2008;11:171-5.
6. INAMI/RIZIV. Info Spot. Het voorschrijven op stofnaam. In; 2008 [monograph on the Internet]. Brussels, Belgium, Rijksinstituut voor ziekte en invaliditeitsverzekering (RIZIV) / l'institut national d'assurance maladie invalidité (INAMI) [cited 2011 May 13]. Available from: www.riziv.fgov.be/drug/nl/statistics-scientific-information/pharmanet/info-spot/2008-03-27/pdf/infospot20080327.pdf