Paediatricians from Europe are concerned about the extrapolation of the limited amount of available clinical data from adults with rheumatologic diseases to children with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) [1].
European paediatricians advocate biosimilar trials in children with IBD
Biosimilars/General
|
Posted 09/10/2015
 0
Post your comment
0
Post your comment
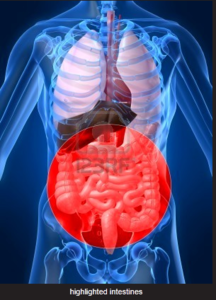
Members of the Paediatric IBD Porto Group of the European Society for Paediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology and Nutrition (ESPGHAN) came together to provide consensus-based recommendations specifically for paediatric gastroenterologists treating children with IBD.
Concerns over extrapolation stem from the fact that children with IBD on average have a more severe disease phenotype than in adult-onset IBD, potentially requiring anti-TNF treatment for a longer duration.
The group therefore believes that any extrapolation to IBD in children should be done with caution and needs some consideration. They also believe that post-marketing surveillance programmes for efficacy, safety and immunogenicity should become mandatory in children with IBD using biosimilars, as for all biological drugs.
The recommendations proposed by the group have been provided as an addition to the European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) position statement [2] and include the following statements:
- EMA approved the use of biosimilars for infliximab for all indications, including adult and paediatric IBD. The ESPGHAN Paediatric IBD Porto Group advocates giving high priority to performing paediatric trials with long-term follow-up to support this decision.
- Treatment of a child with sustained remission on a specific medication should not be switched to a biosimilar until clinical trials in IBD are available to support the safety and efficacy of such a change.
- Post-marketing surveillance programmes for efficacy, safety and immunogenicity in children with IBD should be a mandatory requirement for the marketing of biologicals and biosimilars with respective indications.
The group states that due to the absence of published trials on the usage of biosimilars in adult and paediatric IBD the statements cannot be used as recommendations for management. They reflect expert opinion designed to inform paediatric gastroenterologists and to promote consensus on proper usage of these agents in children with IBD.
Conflict of Interest
Several of the authors of the research paper [1] reported conflicts of interest, including having received consultation fees, research grants and honoraria from originator biologicals and biosimilars manufacturers. For full details of the authors’ conflicts of interest, see the research paper [1].
Related article
Spanish Society of Rheumatology issues position statement on biosimilars
References
1. de Ridder L, et al. Use of biosimilars in paediatric inflammatory bowel disease: a position statement of the ESPGHAN Paediatric IBD Porto Group. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2015 Jul 6. [Epub ahead of print].
2. GaBI Online - Generics and Biosimilars Initiative. ECCO position statement on biosimilars [www.gabionline.net]. Mol, Belgium: Pro Pharma Communications International; [cited 2015 Oct 9]. Available from: www.gabionline.net/Biosimilars/General/ECCO-position-statement-on-biosimilars
Permission granted to reproduce for personal and non-commercial use only. All other reproduction, copy or reprinting of all or part of any ‘Content’ found on this website is strictly prohibited without the prior consent of the publisher. Contact the publisher to obtain permission before redistributing.
Copyright – Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are © 2015 Pro Pharma Communications International. All Rights Reserved.
Research
Reaching ESG goals in pharmaceutical development
What is the future for the US biosimilar interchangeability designation
News
FDA approves third interchangeable ranibizumab biosimilar Nufymco
FDA approves Poherdy (first interchangeable pertuzumab) and Armlupeg (pegfilgrastim) biosimilars
Most viewed articles
The best selling biotechnology drugs of 2008: the next biosimilars targets
Global biosimilars guideline development – EGA’s perspective
Related content
Samsung Bioepis wins Pyzchiva case; Regeneron patent rulings threaten foreign biosimilars
Chinese biosimilars go global: growth, partnerships, and challenges
Stelara biosimilars enter US market with 85% discount in 2025
IFPMA publishes position on pharmacy-mediated substitution for biosimilars
Samsung Bioepis wins Pyzchiva case; Regeneron patent rulings threaten foreign biosimilars

Biosimilars/General Posted 30/07/2025
Chinese biosimilars go global: growth, partnerships, and challenges
Biosimilars/General Posted 30/04/2025
IFPMA publishes position on pharmacy-mediated substitution for biosimilars

Biosimilars/General Posted 21/03/2025
The best selling biotechnology drugs of 2008: the next biosimilars targets







Post your comment