In the EU there are several different routes to marketing authorisation for generic drugs.
Centralised Procedure
Marketing authorisation is issued by the EMA and is valid for the entire EU/European Economic Area.
This procedure is optional for generics:
- if the reference product is authorised via a centralised procedure (CP)
- if a CP is in the interests of patients at a EU level.
Mutual Recognition Procedure/Decentralised Procedure
This is the only route available for generic drugs if the reference product is authorised nationally.
The CMDh (Co-ordination Group for Mutual Recognition and Decentralised Procedures – Human) is responsible for the examination of any question relating to marketing authorisation of a medicinal product in two or more Member States in accordance with the Mutual Recognition Procedure (MRP) or the Decentralised Procedure (DCP).
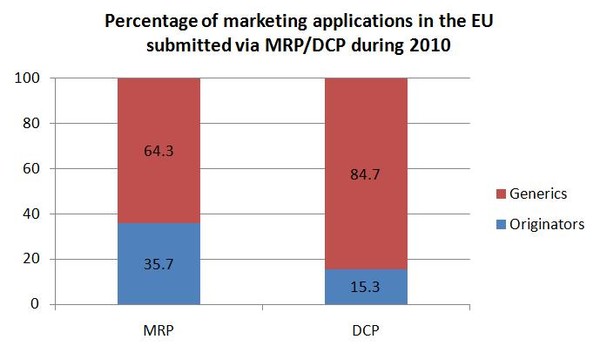
Generic medicines account for the majority of marketing authorisation submissions in the DCP and MRP. Generic applications in 2010 accounted for 64.3% of MRPs and a staggering 84.7% of DCPs.
National procedure
This is only applicable if the generic submission is carried out in only one country. Marketing authorisation will then only be applicable to that one country. This can in some cases be done prior to a MRP.
Related articles
A sustainable generics industry in the EU
The role of generic drugs in the EU
Generic drugs – registration, quality, value and sustainability
Quality control for generic drugs
Generic applications in the EU, patents and exclusivity
Source: CMDh annual report 2010, EGA, EU Official Journal








 0
0









Post your comment