Health spending fell across the EU in 2010, governments affected by continuing austerity measures tried to save money by reducing spending on health, according to Health at a Glance: Europe 2012, a new joint report by the OECD and the European Commission.
EU health spending in 2010 decreases for first time since 1975
Home/Reports
|
Posted 14/12/2012
 0
Post your comment
0
Post your comment
This drop in spending per person and as a percentage of gross domestic product (GDP) reverses increases seen in the years before the economic crisis, when health spending per person grew two or three times faster than incomes in many countries. From an annual average growth rate of 4.6% between 2000 and 2009, health spending per person fell to ‑0.6% in 2010. This is the first time health spending has fallen in Europe since 1975.
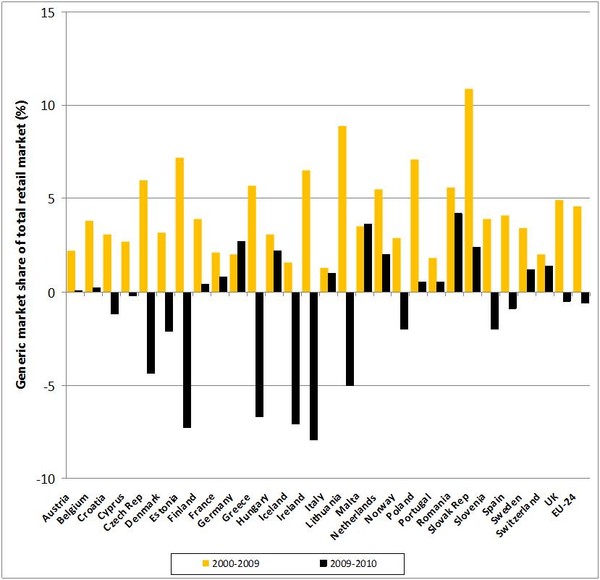
Health spending as a share of GDP was highest in The Netherlands (12%) in 2010, followed by France and Germany (11.6%). The share of GDP allocated to health was 9.0% on average across EU countries, down from 9.2% in 2009, see Figure 1.
Figure 1: Annual average growth rate in health expenditure per capita, in real terms, 2000 to 2010 (or nearest year) [1]
Countries most affected by the economic crisis showed the highest reductions in spending on health. In Ireland, health spending fell 7.9% in 2010, compared with an average annual growth rate of 6.5% between 2000 and 2009. In Estonia, health expenditure per person dropped by 7.3% in 2010, following growth of over 7% per year from 2000 to 2009, with reductions in both public and private spending. In Greece, estimates suggest that health spending per person fell 6.7% in 2010, reversing annual growth of 5.7% between 2000 and 2009.
The report found that public health and prevention programmes had suffered the greatest decreases. On average across EU countries, only 3% of a shrinking health budget was allocated to prevention and public health programmes in areas such as immunisation, smoking, alcohol drinking, nutrition and physical activity, 3.2% less than the year before.
The report cautions that the reduction or slowdown in spending in nearly all EU countries may have a long-term impact on healthcare outcomes.
Related article
Generic drug prices decrease, brand-name prices increase
Reference
1. OECD [homepage on the Internet]. Health at a Glance: Europe 2012 (based on OECD Health Data 2012; Eurostat Statistics Database: WHO Global Expenditure Database). 2012 [cited 2012 Dec 14]. Available from: http://www.oecd.org/health/healthataglanceeurope.htm
Permission granted to reproduce for personal and educational use only. All other reproduction, copy or reprinting of all or part of any ‘Content’ found on this website is strictly prohibited without the prior consent of the publisher. Contact the publisher to obtain permission before redistributing.
Source: Europa, OECD
Guidelines
US guidance to remove biosimilar comparative efficacy studies
New guidance for biologicals in Pakistan and Hong Kong’s independent drug regulatory authority
Policies & Legislation
EU accepts results from FDA GMP inspections for sites outside the US
WHO to remove animal tests and establish 17 reference standards for biologicals
EU steps closer to the ‘tailored approach’ for biosimilars development

Home/Reports Posted 21/11/2025
Advancing biologicals regulation in Argentina: from registration to global harmonization

Home/Reports Posted 10/10/2025
The best selling biotechnology drugs of 2008: the next biosimilars targets






Post your comment