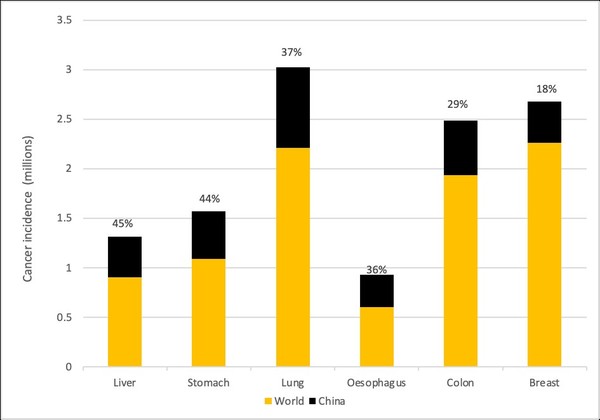
Cancer is the leading cause of death in China and in 2018 the country represented 24% of all cancer incidences and 29-45% of the world’s total for colon, liver, lung, oesophagus and stomach cancers, see Figure 1.
Cancer driving the need for copy biologicals in China
Home/Reports
|
Posted 26/03/2021
 0
Post your comment
0
Post your comment
Cancer prognoses are also poorer, with estimates suggesting that Asia has a higher proportion of cancer deaths (58.3%) compared with their incidence (49.3%) [1]. The situation in China has been alarming partly due to its rapid population growth and socioeconomic development. This is unlikely to change in the foreseeable future, partly due to the aging population and changing lifestyle and dietary habits. In fact, in 2020, more than three million Chinese died of cancer [2].
Figure 1: Cancer incidence in 2020 in China and the World
According to the National Coalition of Cancer Research and Frost & Sullivan, the incidence of cancer is expected to grow at a 2.6% compound annual growth rate (CAGR) from 2017 to 2022 in China, far outpacing the 0.8% expected in the US.
The need for copy biologicals is highlighted by the fact that although therapies for cancer exist, their availability has historically been limited in China. Out of 55 oncology drugs launched globally from 2012 to 2016, only nine were available in China in 2017. The lack of available medication is particularly acute within advanced therapies, such as biologicals, including monoclonal antibodies (mAbs). While eight of the top 10 global bestsellers in 2017 were biologicals, only two of China’s top 10 selling drugs were biologicals and none were oncology drugs. Moreover, China’s mAb sales in 2018 represented less than 2% of the global total (only US$2.0 billion out of over US$110 billion of global mAb sales).
Editor’s comment
European Medicines Agency regulatory requirements ensure the same high standards of quality, safety and efficacy for biosimilars as for originator biologicals, and also include a rigorous comparability exercise with the reference product but they are not universally accepted by regulatory bodies outside of the European Union (EU). It should be noted that copy biologicals approved in China might not have been authorized if they had been subjected to the strict regulatory processes required for approval of biosimilars in the EU.
Related article
Investment increasing pipeline of copy biologicals in China
Improved regulation favouring copy biologicals in China
Patent expiries may drive development of copy biologicals in China
The state of play for copy biologicals in China
| LATIN AMERICAN FORUM – Coming soon! To further enhance the objectives of GaBI in sharing information and knowledge that ensure policies supportive of safe biosimilars use, we are pleased to announce that we will be launching a new section on GaBI Online and GaBI Journal, the ‘Latin American Forum’ (in Spanish) featuring the latest news and updates on research and developments in generic and biosimilar medicines in Latin America. Register to receive the GaBI Latin American Forum newsletter. Inform colleagues and friends of this new initiative.
LATIN AMERICAN FORUM – Próximamente! Para fomentar los objetivos de GaBI sobre la difusión de información y conocimiento sobre las políticas de apoyo que garantizan el uso seguro de medicamentos biosimilares, nos complace anunciar el lanzamiento de una nueva sección en GaBI Online y GaBI Journal, el ‘Latin American Forum’ (en español), que presentará las últimas noticias y actualizaciones en investigación y desarrollo sobre medicamentos genéricos y biosimilares en Latinoamérica. Regístrese para recibir el boletín informativo GaBI Latin American Forum. Informe a colegas y amigos sobre esta nueva iniciativa. |
References
1. Union for International Cancer Control (UICC). Global cancer data: GLOBOCAN 2020 [homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2021 Mar 26]. Available from: https://www.uicc.org/news/globocan-2020-new-global-cancer-data
2. World Health Organization (WHO), International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). China factsheet [homepage on the Internet]. [cited 2021 Mar 26]. Available from: www.gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/populations/160-china-fact-sheets.pdf
Permission granted to reproduce for personal and non-commercial use only. All other reproduction, copy or reprinting of all or part of any ‘Content’ found on this website is strictly prohibited without the prior consent of the publisher. Contact the publisher to obtain permission before redistributing.
Copyright – Unless otherwise stated all contents of this website are © 2021 Pro Pharma Communications International. All Rights Reserved.
Source: Hogan Lovells, IARC, WHO
Guidelines
US guidance to remove biosimilar comparative efficacy studies
New guidance for biologicals in Pakistan and Hong Kong’s independent drug regulatory authority
Policies & Legislation
EU accepts results from FDA GMP inspections for sites outside the US
WHO to remove animal tests and establish 17 reference standards for biologicals
EU steps closer to the ‘tailored approach’ for biosimilars development

Home/Reports Posted 21/11/2025
Advancing biologicals regulation in Argentina: from registration to global harmonization

Home/Reports Posted 10/10/2025
The best selling biotechnology drugs of 2008: the next biosimilars targets






Post your comment